class test{
private LocationPojo preLocation;
private List<LocationPojo> nowLocation;
private Long preTime;
public boolean test(List<LocationPojo> now,LocationPojo pre) {
this.nowLocation = now;
this.preLocation = pre;
double distance = 0;//两点坐标点距离
int tmp = 40;//精准度上行初始阀值(固定)
int AccuracyThresholdUp = tmp;//精准度上行阀值
int AccuracyThresholdDown = 30;//精准度下行阀值
int stopCount = 0; //静止状态坐标计数
int rectCountDown = 0; //坐标在30M围栏内计数
int rectCountUp = 0; //坐标在100M围栏外计数
int notCheckUpCount = 0; //超出大围栏计数,不检查精准度
/*
*
* 如果没有上一次的GPS数据,那么直接返回这次的GPS数据。
**/
if (this.preLocation() == null){
this.preLocation(this.nowLocation.get(0));
this.preTime = this.preLocation().getAddTime();//上一次记录的时间
return true;
}
LocationPojo b = null;
//循环计数(我这边是每次定位间隔是1秒,每次定位数据达到10条后进入计算,所以有这个循环)
//就是用10条现在的GPS数据与上一次的GPS数据,进行数据计算。
for (LocationPojo pojo:this.nowLocation){
if (b == null){
b = pojo;
}
//判断不是GPS数据,如果不是,改变阀值的上下值
if (pojo.getProvider().equals(GPS.GPS)) {
AccuracyThresholdUp = (int)(tmp * 1.5);//网络定位普遍在40以上,所以需要改变精准度的阀值。
}else{
AccuracyThresholdUp = tmp;//由于是循环的,所以每次都需要重新赋值。
}
//没有速度,或者有速度但是精准度很高,我会把这类的数据归于静止状态(GPS漂移数据)
if (pojo.getSpeed() <= 0 || (pojo.getSpeed() > 0 && pojo.getAccuracy() > AccuracyThresholdDown)){
stopCount++;
}
//测算距离(测算距离的方法有很多,我现在把它封装成工具类了)
distance = CommUtils.getLocationDistance(pojo.getLatitude(),pojo.getLongitude(),preLocation.getLatitude(),preLocation.getLongitude());
//优化速度精准度
if(pojo.getSpeed() > 0 && distance > 0){
//距离 / 时间 * 3.6 = 速度(KM)
// float speed = CommUtils.fromatNumber(distance / ((pojo.getAddTime() - this.preTime) / 1000) * 3.6,null);
// pojo.setSpeed(speed);
pojo.setSpeed(CommUtils.formatNumber(pojo.getSpeed().doubleValue(),"#0.00").floatValue());
}
//latlnt电子围栏 30 - 100m
//超出围栏(条件是:lat或者lnt与上一次坐标匹配大于[100m]并且精确度在30m以内,条件成立)
if (distance > 100){
notCheckUpCount++;
//高精准度(GPS数据应该是可靠的)
if(pojo.getAccuracy() < AccuracyThresholdUp){
rectCountUp++;
//如果上一次GPS精准度大于这一次,那么次数GPS数据是有效的。
if(pojo.getAccuracy() <= preLocation.getAccuracy()){
b = pojo;
}
}
}else if (distance > 30 && pojo.getAccuracy() < AccuracyThresholdUp){
//如果在电子围栏内,并且精确度在30m以内,条件成立
rectCountDown++;
if(pojo.getAccuracy() <= preLocation.getAccuracy()){
b = pojo;
}
}
}
//a:在30米的围栏中必须有速度值,而且超出小围栏的计数>=5个,条件成立则正在移动(30M直径的正方形)
//a1:在100米的围栏中有8个条数据均超出,不管有没有速度,条件均成立(也许他是坐飞机,也许他瞬移)
double a = getNowLocation().size() * 0.5;
double a1 = getNowLocation().size() * 0.8;
if ((stopCount <= 5 && rectCountDown >= a) || rectCountUp >= a1 || (notCheckUpCount == getNowLocation().size() && rectCountUp >= a) || (stopCount >= a && rectCountUp >= a)){
this.setPreLocation(b);
this.setPreTime(b.getAddTime());
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
Spring Batch 批处理框架使用介绍
Spring Batch 是一个轻量级的、完善的批处理框架,旨在帮助企业建立健壮、高效的批处理应用。Spring Batch是Spring的一个子项目,使用Java语言并基于Spring框架为基础开发,使得已经使用 Spring 框架的开发者或者企业更容易访问和利用企业服务。
Spring Batch 提供了大量可重用的组件,包括了日志、追踪、事务、任务作业统计、任务重启、跳过、重复、资源管理。对于大数据量和高性能的批处理任务,Spring Batch 同样提供了高级功能和特性来支持,比如分区功能、远程功能。总之,通过 Spring Batch 能够支持简单的、复杂的和大数据量的批处理作业。
Spring Batch 是一个批处理应用框架,不是调度框架,但需要和调度框架合作来构建完成的批处理任务。它只关注批处理任务相关的问题,如事务、并发、监控、执行等,并不提供相应的调度功能。如果需要使用调用框架,在商业软件和开源软件中已经有很多优秀的企业级调度框架(如 Quartz、Tivoli、Control-M、Cron 等)可以使用。
1.现在实现Spring Batch方法,首先是配置:
@Configuration
@EnableBatchProcessing
public class SpringBatchConfiguration {
@Resource
private DataSource dataSource;
@Resource
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
/**
* 任务仓库
* @return
*/
@Bean
public JobRepository jobRepository() throws Exception{
JobRepositoryFactoryBean jobRepositoryFactoryBean = new JobRepositoryFactoryBean();
jobRepositoryFactoryBean.setTransactionManager(transactionManager);
jobRepositoryFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
jobRepositoryFactoryBean.setDatabaseType("mysql");
return jobRepositoryFactoryBean.getObject();
}
/**
* 任务加载器
* @return
*/
@Bean
public SimpleJobLauncher jobLauncher() throws Exception{
SimpleJobLauncher launcher = new SimpleJobLauncher();
launcher.setJobRepository(this.jobRepository());
return launcher;
}
@Bean
public TestJobListener testJobListener(){
return new TestJobListener();
}
}
2.TestJobListener监听器
public class TestJobListener implements JobExecutionListener {
private final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(this.getClass().getName());
private long time = 0L;
@Override
public void beforeJob(JobExecution jobExecution) {
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis();
logger.info(">>job start");
}
@Override
public void afterJob(JobExecution jobExecution) {
logger.info(">>job end("+(System.currentTimeMillis()-time)+")");
}
}
3.读操作代码
public class TestItemReader2 extends FlatFileItemReader<BikeKey> { public TestItemReader2(){ } public void setData(String path,LineMapper<BikeKey> lineMapper){ this.setResource(new FileSystemResource(path)); this.setLineMapper(lineMapper); } } //LineMapper代码@Component public class TestItemLineMapper implements LineMapper<BikeKey> { @Override public BikeKey mapLine(String s, int i) throws Exception { System.out.println("mapLine..."+s+" i:"+i); String[] args = s.split(","); // 创建DeviceCommand对象 BikeKey bikeKey = new BikeKey(); bikeKey.setId(null); bikeKey.setStatus(0); bikeKey.setKeySn(args[1]); return bikeKey; } }
4.写操作代码
@Component
public class TestItemWriter implements ItemWriter<BikeKey> {
@Resource
private IBikeKeyService bikeKeyService;
@Override
public void write(List<? extends BikeKey> list) throws Exception {
for (int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println("write..."+list.size()+" i:"+i);
bikeKeyService.insert(list.get(i));
}
}
}
5.处理过程代码
@Component
public class TestItemProcessor implements ItemProcessor<BikeKey,BikeKey> {
@Override
public BikeKey process(BikeKey bikeKey) throws Exception {
System.out.println("process...");
bikeKey.setKeyCreateTime((int) (DateUtil.getTime()/1000));
return bikeKey;
}
}
6.工作统一调用代码
@Component
public class TestDoImport {
@Resource
private JobLauncher jobLauncher;
@Resource
private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory;
@Resource
private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory;
@Resource
private TestJobListener jobListener;
@Resource
private TestItemLineMapper lineMapper;
/**
* 读操作
*/
private TestItemReader2 reader;
/**
* 写操作
*/
@Resource
private TestItemWriter writer;
/**
* 处理过程
*/
@Resource
private TestItemProcessor processor;
public TestDoImport(){
}
public void doImport(){
/**
* 批量任务的参数
*/
JobParameters jobParameters = new JobParametersBuilder()
.addLong("TIME",System.currentTimeMillis())
.toJobParameters();
try {
/**
* 设置数据路径
*/
reader = new TestItemReader2();
reader.setData("d:/bike_key.csv",lineMapper);
/**
* 执行任务
*/
jobLauncher.run(this.getJob(jobBuilderFactory,this.getStep(stepBuilderFactory,reader,writer,processor)),jobParameters);
} catch (JobExecutionAlreadyRunningException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (JobRestartException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (JobInstanceAlreadyCompleteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (JobParametersInvalidException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取一个工作实例
* @param jobs
* @param step
* @return
*/
private Job getJob(JobBuilderFactory jobs, Step step){
return jobs
.get("importJob")
.incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer())
.flow(step)
.end()
.listener(jobListener)//监听整个过程
.build();
}
/**
* 获取一个步骤实例
* @param stepBuilderFactory
* @param reader 读
* @param writer 写
* @param processor 过程
* @return
*/
private Step getStep(StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory, ItemReader<BikeKey> reader, ItemWriter<BikeKey> writer, ItemProcessor<BikeKey,BikeKey> processor){
return stepBuilderFactory
.get("step1")
.<BikeKey,BikeKey> chunk(1)
.reader(reader)
.processor(processor)
.writer(writer)
.build();
}
}
运行日志:
23-May-2018 13:42:03.817 信息 [http-nio-8080-exec-6] com.mymvc.system.batch.listener.TestJobListener.beforeJob >>job start
mapLine…,a0011 i:1
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a0022 i:2
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a0033 i:3
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a0044 i:4
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a0055 i:5
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a0016 i:6
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a0027 i:7
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a0038 i:8
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a0049 i:9
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00510 i:10
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00111 i:11
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00212 i:12
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00313 i:13
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00414 i:14
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00515 i:15
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00116 i:16
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00217 i:17
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00318 i:18
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00419 i:19
process…
write…1 i:0
mapLine…,a00520 i:20
process…
write…1 i:0
23-May-2018 13:42:05.252 信息 [http-nio-8080-exec-6] com.mymvc.system.batch.listener.TestJobListener.afterJob >>job end(1435)
Spring Batch 批处理框架介绍
前言
在大型的企业应用中,或多或少都会存在大量的任务需要处理,如邮件批量通知所有将要过期的会员等等。而在批量处理任务的过程中,又需要注意很多细节,如任务异常、性能瓶颈等等。那么,使用一款优秀的框架总比我们自己重复地造轮子要好得多一些。
我所在的物联网云平台部门就有这么一个需求,需要实现批量下发命令给百万设备。为了防止枯燥乏味,下面就让我们先通过Spring Batch框架简单地实现一下这个功能,再来详细地介绍这款框架!
小试牛刀
Demo代码:https://github.com/wudashan/spring-batch-demo.git
引入依赖
首先我们需要引入对Spring Batch的依赖,在pom.xml文件加入下面的代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.batch</groupId> <artifactId>spring-batch-core</artifactId> <version>3.0.8.RELEASE</version></dependency> |
装载Bean
其次,我们需要在resources目录下,创建applicationContext.xml文件,用于自动注入我们需要的类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.batch.support.transaction.ResourcelessTransactionManager"/> <!-- 任务仓库 --> <bean id="jobRepository" class="org.springframework.batch.core.repository.support.MapJobRepositoryFactoryBean"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/> </bean> <!-- 任务加载器 --> <bean id="jobLauncher" class="org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher"> <property name="jobRepository" ref="jobRepository"/> </bean></beans> |
有了上面声明的transactionManager、jobRepository、jobLauncher,我们就可以执行批量任务啦!不过,我们还需要创建一个任务。在Spring Batch框架中,一个任务Job由一个或者多个步骤Step,而步骤又由读操作Reader、处理操作Processor、写操作Writer组成,下面我们分别创建它们。
创建Reader
既然是读操作,那么肯定要有能读的数据源,方便起见,我们直接在resources目录下创建一个batch-data.csv文件,内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
1,PENDING2,PENDING3,PENDING4,PENDING5,PENDING6,PENDING7,PENDING8,PENDING9,PENDING10,PENDING |
非常简单,其中第一列代表着命令的id,第二列代表着命令的当前状态。也就是说,现在有10条缓存的命令,需要下发给设备。
读操作需要实现ItemReader<T>接口,框架提供了一个现成的实现类FlatFileItemReader。使用该类需要设置Resource和LineMapper。Resource代表着数据源,即我们的batch-data.csv文件;LineMapper则表示如何将文件的每行数据转成对应的DTO对象。
创建DTO对象
由于我们的数据源是命令数据,所以我们需要创建一个DeviceCommand.java文件,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public class DeviceCommand { private String id; private String status; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getStatus() { return status; } public void setStatus(String status) { this.status = status; }} |
自定义LineMapper
我们需要自己实现一个LineMapper实现类,用于将batch-data.csv文件的每行数据,转成程序方便处理的DeviceCommand对象。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public class HelloLineMapper implements LineMapper<DeviceCommand> { @Override public DeviceCommand mapLine(String line, int lineNumber) throws Exception { // 逗号分割每一行数据 String[] args = line.split(","); // 创建DeviceCommand对象 DeviceCommand deviceCommand = new DeviceCommand(); // 设置id值到对象中 deviceCommand.setId(args[0]); // 设置status值到对象中 deviceCommand.setStatus(args[1]); // 返回对象 return deviceCommand; }} |
创建Processor
读完数据后,我们就需要处理数据了。既然我们前面从文件里读取了待下发的命令,那么在这里下发命令给设备是最好的时机。处理操作需要实现ItemProcessor<I, O>接口,我们自己实现一个HelloItemProcessor.java即可,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public class HelloItemProcessor implements ItemProcessor<DeviceCommand, DeviceCommand> { @Override public DeviceCommand process(DeviceCommand deviceCommand) throws Exception { // 模拟下发命令给设备 System.out.println("send command to device, id=" + deviceCommand.getId()); // 更新命令状态 deviceCommand.setStatus("SENT"); // 返回命令对象 return deviceCommand; } } |
创建Writer
处理完数据后,我们需要更新命令状态到文件里,用于记录我们已经下发。与读文件类似,我们需要实现ItemWriter<T>接口,框架也提供了一个现成的实现类FlatFileItemWriter。使用该类需要设置Resource和LineAggregator。Resource代表着数据源,即我们的batch-data.csv文件;LineAggregator则表示如何将DTO对象转成字符串保存到文件的每行。
自定义LineAggregator
我们需要自己实现一个LineAggregator实现类,用于将DeviceCommand对象转成字符串,保存到batch-data.csv文件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class HelloLineAggregator implements LineAggregator<DeviceCommand> { @Override public String aggregate(DeviceCommand deviceCommand) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); sb.append(deviceCommand.getId()); sb.append(","); sb.append(deviceCommand.getStatus()); return sb.toString(); }} |
主程序
那么,完事具备,只欠东风!接下面我们在主程序Main.java里实现我们的批量命令下发功能!代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 加载上下文 String[] configLocations = {"applicationContext.xml"}; ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configLocations); // 获取任务启动器 JobLauncher jobLauncher = applicationContext.getBean(JobLauncher.class); JobRepository jobRepository = applicationContext.getBean(JobRepository.class); PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager = applicationContext.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class); // 创建reader FlatFileItemReader<DeviceCommand> flatFileItemReader = new FlatFileItemReader<>(); flatFileItemReader.setResource(new FileSystemResource("src/main/resources/batch-data.csv")); flatFileItemReader.setLineMapper(new HelloLineMapper()); // 创建processor HelloItemProcessor helloItemProcessor = new HelloItemProcessor(); // 创建writer FlatFileItemWriter<DeviceCommand> flatFileItemWriter = new FlatFileItemWriter<>(); flatFileItemWriter.setResource(new FileSystemResource("src/main/resources/batch-data.csv")); flatFileItemWriter.setLineAggregator(new HelloLineAggregator()); // 创建Step StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory = new StepBuilderFactory(jobRepository, transactionManager); Step step = stepBuilderFactory.get("step") .<DeviceCommand, DeviceCommand>chunk(1) .reader(flatFileItemReader) // 读操作 .processor(helloItemProcessor) // 处理操作 .writer(flatFileItemWriter) // 写操作 .build(); // 创建Job JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory = new JobBuilderFactory(jobRepository); Job job = jobBuilderFactory.get("job") .start(step) .build(); // 启动任务 jobLauncher.run(job, new JobParameters()); }} |
执行main方法之后,屏幕将会输出下面信息:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
send command to device, id=1send command to device, id=2send command to device, id=3send command to device, id=4send command to device, id=5send command to device, id=6send command to device, id=7send command to device, id=8send command to device, id=9send command to device, id=10 |
再查看batch-data.csv文件,将会发现命令状态全部更新为SENT:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
1,SENT2,SENT3,SENT4,SENT5,SENT6,SENT7,SENT8,SENT9,SENT10,SENT |
至此,我们的批量命令下发全部成功!可以发现,使用Spring Batch框架来实现批处理非常的轻量,当然这只是它所有功能里的冰山一角。
正式介绍
Spring Batch在官网是这样一句话介绍自己的:A lightweight, comprehensive batch framework designed to enable the development of robust batch applications vital for the daily operations of enterprise systems.(一款轻量的、全面的批处理框架,用于开发强大的日常运营的企业级批处理应用程序。)
框架主要有以下功能:
- Transaction management(事务管理)
- Chunk based processing(基于块的处理)
- Declarative I/O(声明式的输入输出)
- Start/Stop/Restart(启动/停止/再启动)
- Retry/Skip(重试/跳过)
如果你的批处理程序需要使用上面的功能,那就大胆地使用它吧!
框架全貌
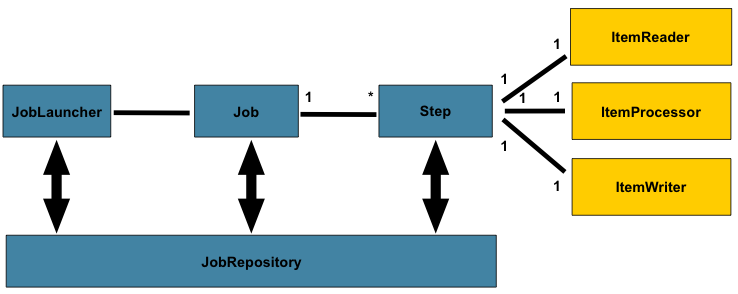
框架一共有4个主要角色:JobLauncher是任务启动器,通过它来启动任务,可以看做是程序的入口。Job代表着一个具体的任务。Step代表着一个具体的步骤,一个Job可以包含多个Step(想象把大象放进冰箱这个任务需要多少个步骤你就明白了)。JobRepository是存储数据的地方,可以看做是一个数据库的接口,在任务执行的时候需要通过它来记录任务状态等等信息。
JobLauncher
JobLauncher是任务启动器,该接口只有一个run方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface JobLauncher { public JobExecution run(Job job, JobParameters jobParameters) throws JobExecutionAlreadyRunningException, JobRestartException, JobInstanceAlreadyCompleteException, JobParametersInvalidException;} |
除了传入Job对象之外,还需要传入JobParameters对象,后续讲到Job再解释为什么要多传一个JobParameters。通过JobLauncher可以在Java程序中调用批处理任务,也可以通过命令行或者其他框架(如定时调度框架Quartz、Web后台框架Spring MVC)中调用批处理任务。Spring Batch框架提供了一个JobLauncher的实现类SimpleJobLauncher。
Job
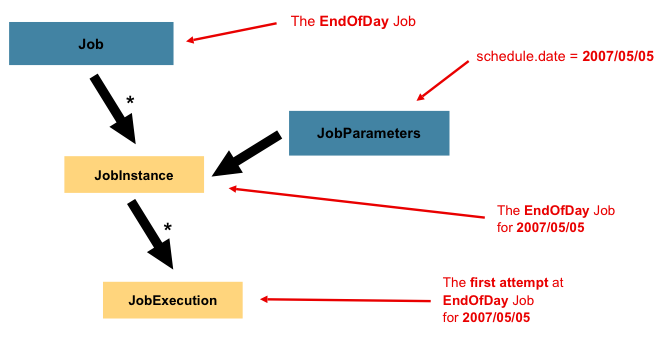
Job代表着一个任务,一个Job与一个或者多个JobInstance相关联,而一个JobInstance又与一个或者多个JobExecution相关联:
考虑到任务可能不是只执行一次就再也不执行了,更多的情况可能是定时任务,如每天执行一次,每个星期执行一次等等,那么为了区分每次执行的任务,框架使用了JobInstance。如上图所示,Job是一个EndOfDay(每天最后时刻执行的任务),那么其中一个JobInstance就代表着2007年5月5日那天执行的任务实例。框架通过在执行JobLauncher.run(Job, JobParameters)方法时传入的JobParameters来区分是哪一天的任务。
由于2007年5月5日那天执行的任务可能不会一次就执行完成,比如中途被停止,或者出现异常导致中断,需要多执行几次才能完成,所以框架使用了JobExecution来表示每次执行的任务。
Step
一个Job任务可以分为几个Step步骤,与JobExection相同,每次执行Step的时候使用StepExecution来表示执行的步骤。每一个Step还包含着一个ItemReader、ItemProcessor、ItemWriter,下面分别介绍这三者。
ItemReader
ItemReader代表着读操作,其接口如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface ItemReader<T> { T read() throws Exception, UnexpectedInputException, ParseException, NonTransientResourceException;} |
框架已经提供了多种ItemReader接口的实现类,包括对文本文件、XML文件、数据库、JMS消息等读的处理,当然我们也可以自己实现该接口。
ItemProcessor
ItemReader代表着处理操作,其接口如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface ItemProcessor<I, O> { O process(I item) throws Exception;} |
process方法的形参传入I类型的对象,通过处理后返回O型的对象。开发者可以实现自己的业务代码来对数据进行处理。
ItemWriter
ItemReader代表着写操作,其接口如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface ItemWriter<T> { void write(List<? extends T> items) throws Exception;} |
框架已经提供了多种ItemWriter接口的实现类,包括对文本文件、XML文件、数据库、JMS消息等写的处理,当然我们也可以自己实现该接口。
JobRepository
JobRepository用于存储任务执行的状态信息,比如什么时间点执行了什么任务、任务执行结果如何等等。框架提供了2种实现,一种是通过Map形式保存在内存中,当Java程序重启后任务信息也就丢失了,并且在分布式下无法获取其他节点的任务执行情况;另一种是保存在数据库中,并且将数据保存在下面6张表里:
- BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE
- BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_PARAMS
- BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION
- BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION
- BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
Spring Batch框架的JobRepository支持主流的数据库:DB2、Derby、H2、HSQLDB、MySQL、Oracle、PostgreSQL、SQLServer、Sybase。可爱的是,我司的Gauss数据库也是支持的,只不过需要稍加配置。
360全景图three.js与Photo-Sphere-Viewer-master 3D全景浏览开发
1.支持WebGL和canvas的浏览器 (IE10, IE11支持, 但在IE里移动图片时很卡, 不一定是全部人都有这情况)
2.Three.js (文件较大, 有官网demo, 可不下载, 下载photo-sphere-viewer.js时也有three.js)
|
1
|
下载地址:https://github.com/mrdoob/three.js |
3.photo-sphere-viewer.js (这是基于Three.js开发的柱状全景图插件)
|
1
|
下载地址:https://github.com/JeremyHeleine/Photo-Sphere-Viewer |
4.360度全景图,是左右能够完美拼接的
|
1
|
参考: 图片尺寸 3600 * 1800 (最佳尺寸) http://www.360pano.eu/show/?id=400 |
5.引入js
6.js调用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
var div = document.getElementById('container');var PSV = new PhotoSphereViewer({ // Path to the panorama panorama: 'images/0398.jpg', // Container container: div, // Deactivate the animation time_anim: false, // Display the navigation bar navbar: true, // Resize the panorama size: { width: '800px', height: '400px' }, // 限制顶部 // tilt_up_max: Math.PI / 7, // 限制底部 // tilt_down_max: Math.PI / 7 }); |
7.API选择, 配置参数介绍
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
panorama:(必选)全景图的路径。container:(必选)放置全景图的容器。autoload:(默认为true)true为自动加载全景图,false为迟点加载全景图(通.过load方法)。usexmpdata:(默认值为true)photo sphere viewer是否必须读入xmp数据,false为不必须。cors_anonymous:(默认值为true)true为不能通过cookies获得用户pano_size:(默认值为null)全景图的大小,是否裁切。default_position:(默认值为0)定义默认位置,用户看见的第一个点,例如:{long: math.pi, lat: math.pi/2}。min_fov:(默认值为30)观察的最小区域,单位degrees,在1-179之间。max_fov:(默认值为90)观察的最大区域,单位degrees,在1-179之间。allow_user_interactions:(默认值为true)设置为false,则禁止用户和全景图交互(导航条不可用)。allow_scroll_to_zoom:(默认值为true)若设置为false,则用户不能通过鼠标滚动进行缩放图片。tilt_up_max:(默认值为math.pi/2)向上倾斜的最大角度,单位radians。tilt_down_max:(默认值为math.pi/2)向下倾斜的最大角度,单位radians。min_longitude:(默认值为0)能够展示的最小经度。max_longitude:(默认值为2PI)能够展示的最大维度。zoome_level:(默认值为0)默认的缩放级别,值在0-100之间。long_offset:(默认值为PI/360)mouse/touch移动时每像素经过的经度值。lat_offset:(默认值为pi/180)mouse/touch移动时每像素经过的纬度值。time_anim(默认值为2000)全景图在time_anim毫秒后会自动进行动画。(设置为false禁用它)reverse_anim:(默认值为true)当水平方向到达最大/最小的经度时,动画方向是否反转(仅仅是不能看到完整的圆)。anim_speed:(默认值为2rpm)动画每秒/分钟多少的速度。vertical_anim_speed:(默认值为2rpm)垂直方向的动画每秒/分钟多少的速度。vertical_anim_target:(默认值为0)当自动旋转时的维度,默认为赤道。navbar:(默认为false)显示导航条。navbar_style:(默认值为false)导航条的样式。有效的属性: backgroundColor:导航条背景色(默认值rgba(61, 61, 61, 0.5)); buttonsColor:按钮前景色(默认值 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.7)); buttonBackgroundColor:按钮激活时的背景色(默认值 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.1)); buttonsHeight:按钮高度,单位px(默认值 20); autorotateThickness:自动旋转图片的层(默认值 1); zoomRangeWidth:缩放游标的宽度,单位px(默认值 50); zoomRangeThickness:缩放游标的层(默认值 1); zoomRangeDisk:缩放游标的放大率,单位px(默认值 7); fullscreenRatio:全屏图标的比例(默认值 4/3); fullscreenThickneee:全屏图片的层,单位px(默认值 2)loading_msg:(默认值为Loading...)加载信息。loading_img:(默认值 为null)loading图片的路径。loading_html:(默认值 为null)html加载器(添加到容器中的元素或字符串)。size:(默认值为null)全景图容器的最终尺寸,例如{width: 500, height: 300}。onready:(默认值为null)全景图准备好并且第一张图片展示出来后的回调函数。方法介绍addAction():添加事件(插件没有提供执行事件的方法,似乎是提供给插件内部使用的)。fitToContainer():调整全景图容器大小为指定大小。getPosition():获取坐标经纬度。getPositionInDegrees():获取经纬度度数。getZoomLevel():获取缩放级别。load():加载全景图()。moveTo(longitude, latitude):根据经纬度移动到某一点。rotate(dlong, dlat):根据经纬度度数移动到某一点。toggleAutorotate():是否开启全景图自动旋转。toggleDeviceOrientation():是否开启重力感应方向控制。toggleFullscreen():是否开启全景图全屏。toggleStereo():是否开启立体效果(可用于WebVR哦)。zoom(level):设置缩放级别。zoomIn():放大。zoomOut():缩小。 |
示例参考:https://threejs.org/examples/#webgl_animation_cloth
Apache Mina快速入门
Mina是什么
Mina是一个基于NIO的网络框架,使用它编写程序时,可以专注于业务处理,而不用过于关心IO操作。不论应用程序采用什么协议(TCP、UDP)或者其它的,Mina提供了一套公用的接口,来支持这些协议。目前可以处理的协议有:HTTP, XML, TCP, LDAP, DHCP, NTP, DNS, XMPP, SSH, FTP… 。从这一点来说,Mina不仅仅是一个基于NIO的框架,更是一个网络层协议的实现。



近期评论